Embark on a spiritual journey through Bihar, the birthplace of Buddhism. Discover ancient temples, serene monasteries, and the Bodhi Tree where the Buddha attained enlightenment. Immerse yourself in the rich cultural heritage and spiritual significance of this sacred Indian state.

Introduction
Bihar, a state in eastern India, holds profound significance in the context of Buddhism and the life of Siddhartha Gautama, more commonly known as the Buddha. This region is considered a cradle of spiritual awakening, where pivotal events in the Buddha’s life unfolded, shaping his journey towards enlightenment. It served as the backdrop for his birth in Lumbini, his profound realizations under the Bodhi Tree in Bodh Gaya, and his subsequent teachings in various parts of the state. The rich tapestry of Buddhist history embedded in Bihar is an indelible part of its cultural heritage.
The story of Buddha is intrinsically linked to Bihar, reflecting the state’s importance as a center of religious and philosophical thought. After attaining enlightenment, Buddha delivered his first sermon at Sarnath, located in the outskirts of Varanasi, effectively establishing Bihar as a crucial geographical location in the journey of Buddhism. Both Sarnath and Bodh Gaya are considered vital pilgrimage sites for millions of Buddhists around the world, attracting visitors who seek to immerse themselves in the spiritual essence of the region.
Bihar’s landscape is dotted with stupas, monasteries, and ancient ruins, resonating with the teachings and life events of Buddha. Pilgrims often walk the sacred paths that connect these significant locations, experiencing the ambience that once nurtured his ideals of compassion, mindfulness, and self-realization. The archaeological sites, such as Nalanda University, once an eminent center for Buddhist learning, showcase Bihar’s enduring legacy in disseminating the principles of Buddhism, both locally and internationally.
In essence, Bihar is not merely a geographical entity; it symbolizes the journey of enlightenment, embodying the principles that Buddha espoused. The state’s historical and spiritual significance continues to inspire spiritual seekers and scholars alike, underscoring its status as the land of enlightenment.
Key Locations in Bihar Associated with Buddha
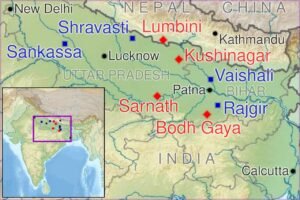
Bihar is a state that holds significant historical and religious importance in the life of Siddhartha Gautama, widely known as Buddha. Several key locations in Bihar are essential for understanding the Buddha’s journey and the development of Buddhism. Among these, Bodh Gaya, Lumbini, Sarnath, and Nalanda stand out prominently for their contributions to Buddhist heritage.
Bodh Gaya is perhaps the most renowned site associated with Buddha, as it is where he attained enlightenment under the Bodhi tree. This transformative event took place around the 5th century BCE and is commemorated at the Mahabodhi Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The temple complex attracts thousands of pilgrims from around the world, who participate in meditation and offerings, providing a vibrant atmosphere of spirituality.
Lumbini, although located in present-day Nepal, is a crucial site connected to Buddha’s life as it is recognized as his birthplace. However, it is often visited in conjunction with Bihar’s sites, highlighting the interconnectedness of various locations tied to the Buddha’s narrative. The sacred gardens, ancient stupas, and the Maya Devi Temple mark this historical area, drawing devotees and tourists alike.
Sarnath is another pivotal location where Buddha delivered his first sermon after attaining enlightenment. The Deer Park at Sarnath is notable for the Dhamek Stupa and the Ashoka Pillar, symbolizing the spread of Buddhism. Today, it serves as a center for pilgrimage and scholarly activities, reflecting on the teachings of the Buddha.
Lastly, Nalanda, once the world’s oldest residential university, stands as a testament to Buddhist education and scholarship. Established in the 5th century CE, it attracted scholars globally, influencing Buddhist studies and philosophy. The ruins of Nalanda University today resonate with history, and ongoing archaeological efforts continue to unearth its rich past.
Buddha’s Teachings and Their Impact on Bihar
Bihar holds a pivotal position in the historical narrative of Buddhism, as it is in this region that Siddhartha Gautama, known as the Buddha, attained enlightenment. The teachings of the Buddha, fundamentally rooted in the pursuit of a greater understanding of existence, fundamentally transformed the societal landscape of Bihar, establishing it as a significant center for spiritual learning. Central to Buddha’s philosophy are the Four Noble Truths, which articulate the nature of suffering and lay the foundation for the path towards liberation.
The Four Noble Truths encompass the acknowledgment of suffering (Dukkha), the origins of suffering stemming from desire and attachment (Samudaya), the cessation of suffering through the relinquishment of these attachments (Nirodha), and the path leading to the end of suffering (Magga). In various sacred sites across Bihar, including Bodh Gaya and Sarnath, the Buddha imparted these teachings to his followers. The Eightfold Path, which serves as a practical guideline for ethical conduct and spiritual growth, further elevated the moral framework of society during that era. This path comprises Right Understanding, Right Intent, Right Speech, Right Action, Right Livelihood, Right Effort, Right Mindfulness, and Right Concentration.
The dissemination of these teachings through Buddhist monasteries and schools in Bihar fostered a cultural renaissance, emphasizing ethical living, compassion, and mindfulness. The principles of Buddhism deeply influenced the art, literature, and architecture of the region. Monuments such as the Mahabodhi Temple and various stupas are not only architectural marvels but also bear testimony to the devotion and philosophical advancements inspired by the Buddha’s teachings. As a result, Bihar emerged as a beacon of hope and enlightenment, shaping not only the local populace but also attracting seekers from distant lands, all drawn by the transformative power of Buddhist philosophy.
Pilgrimage and Tourism in Bihar: The Modern-Day Influence
Bihar, steeped in rich history and cultural significance, stands as a vital pilgrimage destination for Buddhists globally. The state’s historical sites, such as Bodh Gaya, where Siddhartha Gautama attained enlightenment, draw thousands of international visitors annually. These sites not only serve spiritual journeys but also contribute significantly to the local economy through tourism. The influx of pilgrims has spurred growth in infrastructure, including hotels, restaurants, and transport services, thereby bolstering Bihar’s economic landscape.
Efforts to preserve and promote Buddhist heritage are evident through various government and non-government initiatives. The Bihar government has introduced measures aimed at safeguarding critical sites, enhancing visitor experiences, and ensuring that Buddhist teachings and culture are well-represented. In addition to physical preservation, there are numerous programs aimed at educating visitors about the historical importance of these sites. Events like the Buddha Purnima and the International Buddhists Conference not only celebrate Buddhist philosophy but also serve to attract a diverse audience, fostering a sense of global community.
However, the growth of tourism in Bihar is not without its challenges. Local communities often grapple with the balancing act of welcoming visitors while striving to preserve the sanctity of sacred sites. The rise in commercial development sometimes puts pressure on these culturally significant areas, risking their authenticity. Additionally, environmental concerns arise, requiring careful planning to maintain the natural beauty that complements these spiritual sites. As Bihar continues evolving as a pilgrimage hub, it must navigate these complexities to ensureits venerable heritage is honored and safeguarded for future generations.